
Severity: Warning
Message: fopen(/tmp/ci_sessionscfa5f08a1bab1363604c3a8116747f46bb5ae2e20ba083ded467b0150c3883507a330f79): failed to open stream: No space left on device
Filename: drivers/Session_files_driver.php
Line Number: 156
Backtrace:
File: /usr/local/apache2/htdocs/app/controllers/Page.php
Line: 8
Function: __construct
File: /usr/local/apache2/htdocs/index.php
Line: 314
Function: require_once



A person can donate blood either in a licensed blood bank, blood donation camps or at a blood mobile.

Donor fills up the registration form and gives his consent for donation.
Donors Medical History & life style is asked, check up of temperature, blood pressure, pulse and haemoglobin.

Phlebotomist draws unit (350ml/450ml) of blood. A new sterile meedle is used to draw each unit and the needle is destroyed after it has been used. It taked less than 10 min.
Enjoy Snacks and drinks juice to replenish fluids.


Drink plenty of fluids like water, soup and fruit juices to replace the volume lost during donation.

Avoid lifting heavy weights with the donation arm or engaging in strenuous physical activities to prevent complications.
If you feel dizzy, unwell or have cold sweats, follow the steps listed below.
In uncommon situations where fresh bleeding occurs after the plaster is removed, put gentle pressure on the venepuncture site, raise your arm for 3-5 minutes and apply a bandage to the site.
The bandage or the dressing can be removed after 6 hours. If you notice bruising around the venepuncture site, it is usually caused by bleeding into the tissue underneath the skin.
It will usually resolve in a week's time. If you feel pain or discomfort, applying a cold compress to the area may help. If the venepuncture site becomes swollen or blue or you experience pain or numbness in the arm, call the blood bank.
Blood safety means ensuring that it is safe for the donor to donate blood given current health status as well as that donated blood carries minimal risk of adverse effects for the recipient in terms of matching blood groups and is free of Transfusion Transmissible Infections (TTIs). TTIs are infections which occur in a recipient of a blood transfusion if the transfused blood contains a pathogen. Many organisms like bacteria, viruses and parasites can be transmitted through blood transfusions.
The Drugs and Cosmetics Act of India mandates that all blood units that are collected in blood banks for the purpose of transfusion should be screened for the following organisms:
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Virus
Treponema Pallidum (which causes Syphilis)
Plasmodium species (which causes Malaria)
Blood which is detected as having any of these infections is destroyed to prevent infecting others.
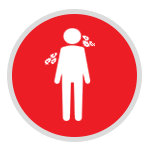
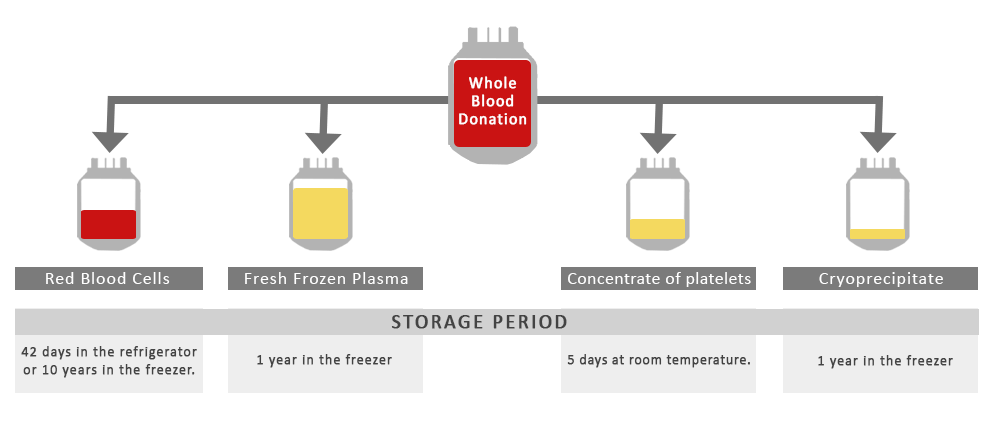
Blood is often separated into its individual components, so patients can be given what they need, for example red blood cells or platelets.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) contain haemoglobin, which distributes oxygen to body tissues, and carries waste carbon dioxide back to the lungs. RBCs are transfused in case of trauma cases, surgery or to treat severe anemia.
Platelets are crucial in helping blood to clot: they do this by clumping together to stop bleeding after an injury.
Plasma is the fluid that carries all blood cells and components. Plasma contains a large number of proteins and substances which are often important ingredients in medical procedures. Plasma is transfused to patients to treat shock due to plasma loss from burns or massive bleeding.
Plasma includes:
Albumin - a protein useful for treating kidney and liver disease
Clotting factors - used to treat types of haemophilia and diseases where blood doesn't clot properly
Immunoglobins - these antibodies help protect against infections
Issuing of Blood components
On request generated by authorized medical personnel your blood components will be issued to a recipient subject to blood group compatibility and blood bank inventory protocols.
